High-Entropy Alloy Powder – HEA

High-Entropy Alloy Powder | HEA
Material: WMoTaNbZr, AlCoCrFeNi, FeMnCoCrC, CoCrNi, NiCrAlY, or Customized.
Production Method: WA, GA, PREP, etc.
High-entropy Alloy Powder is prepared by advanced production methods (e.g., gas atomization, plasma rotating electrode, etc.). We can adjust the composition and ratio according to specific requirements and offer various particle size distributions. As a leading supplier and manufacturer of premium high-entropy alloy products, Heeger Materials leverages advanced technology to deliver high-quality high-entropy alloy powders for various applications.
Or email us at sales@heegermaterials.com.High-Entropy Alloy Powder Data Sheet
| Material: | WMoTaNbZr, WMoTaNbV, AlCoCrFeNi, FeMnCoCrC, CoCrNi, NiCrAlY, FeMnAlCrTi, FeCrCu, NiAlMo, or Customized. |
| Particle Size Distribution: | 15-45μm, 15-53μm, 45-75μm, 45-105μm, 75-150μm, or Customized. |
| Production Method: | Water Atomization (WA) Gas Atomization (GA) Plasma Rotating Electrode Process (PREP) Radio Frequency Plasma Spheroidization |
| Morphology: | Spherical Powder, or Non-Spherical Powder |
What Is A High-Entropy Alloy?
High-entropy alloys (HEAs) are new materials typically composed of five or more metals in equal or near-equal proportions, exhibiting exceptional properties. The four core effects of HEAs work together to distinguish them from traditional alloys:
- High-Entropy Effect: Due to the near-equimolar mixing of multiple elements, the configurational entropy of high-entropy alloys is significantly increased, typically ≥1.5R (R is the gas constant). This high-entropy effect promotes the stability of a single solid-solution phase (such as FCC or BCC structures) while suppressing the formation of complex compounds or intermetallics. It does so by lowering the Gibbs free energy of the system (ΔG = ΔH – TΔS), enhancing the thermodynamic stability of the solid-solution phase at high temperatures.
- Lattice Distortion Effect: The differences in atomic size and chemical properties among the constituent elements in HEAs cause significant lattice distortion. This distortion enhances solid-solution strengthening, boosting the alloy’s strength and hardness, while also slowing atomic diffusion rates, which improves creep resistance and thermal stability.
- Sluggish Diffusion Effect: The complexity arising from the multi-element composition results in slower atomic diffusion rates in HEAs compared to conventional alloys. This sluggish diffusion effect delays phase separation, grain growth, and microstructural evolution, thereby enhancing stability at elevated temperatures and extending service life.
- Cocktail Effect: The synergistic interaction of multiple elements produces unexpected combinations of properties, much like blending ingredients in a cocktail to create a unique flavor. This effect allows HEAs to integrate the strengths of individual elements (e.g., strength, ductility, corrosion resistance), often surpassing the performance limits of single-element systems and exhibiting a wide range of functional characteristics.
Classified according to the number of elements and entropy value, there are also medium-entropy alloys and low-entropy alloys. Medium entropy alloys typically consist of 3-4 elements, with an entropy value ranging from 1.0R to 1.5R, offering a balance between strength and toughness. In contrast, low entropy alloys are similar to traditional alloys, typically containing 1-2 primary elements, and exhibit more homogeneous properties. The key differences are summarized as follows:
| Property | High-entropy Alloys (HEAs) | Medium-entropy Alloys (MEAs) | Low-entropy Alloys (LEAs) |
| Number of Elements | 5 or more | 3 to 4 | 1 to 2 |
| Entropy Value | High (≥1.5R) | Medium (1R~1.5R) | Low (<1R) |
| Microstructure | Simple solid solution | Simple solid solution | May form complex phases |
| Performance | High strength, high-temperature resistance, corrosion resistance | Performance between HEAs and LEAs | Relatively simple performance |
| Typical Applications | Aerospace, energy, and chemical industries | Structural materials, wear-resistant coatings | Construction, automotive, machinery manufacturing |
High-Entropy Alloy Powder
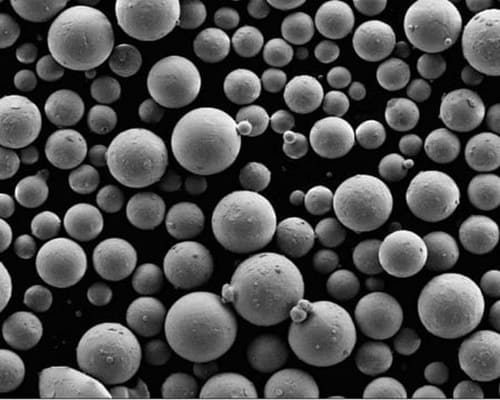
High-entropy Alloy Powders are made of 5 or more equal or custom proportions of metal elements through advanced production methods (e.g., water atomization (WA), gas atomization (GA), plasma rotating electrode process (PREP), radio frequency plasma spheroidization, etc.) to ensure high sphericity, uniform particle size distribution, and excellent purity of the powder. They are widely used in additive manufacturing, thermal spraying, surface engineering, and powder metallurgy. HM can supply customized solutions for the composition, ratio, and particle size distribution to meet specific requirements.

High-Entropy Alloy Powder Products List
| Reference | Product Name | Reference | Product Name | Particle Size Description |
| HMSP2677 | CoCrFeNiMn High-entropy Alloy Powder | Cantor Alloy Spherical Powder | SP-1961 | HfNbZrTi Spherical High-entropy Alloy Powder | 5-25μm(D10=5~10μm, D50=15~20μm, D90=20~25μm) 15-45μm(D10=15~20μm,D50=25~30μm,D90=35~40μm) 15-53μm(D10=15~20μm,D50=25~35μm,D90=45~50μm) 45-75μm(D10=45~55μm,D50=55~65μm,D90=70~75μm) 45-105μm(D10=50~60μm,D50=75~85μm,D90=95~105μm) 75-150μm(D10=80~90μm,D50=110~125μm,D90=135~150μm) 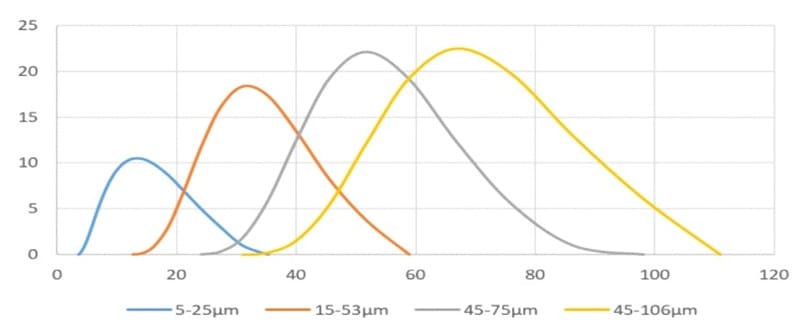 |
| HEA-SP | V-Nb-Mo-Ta-W Refractory HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1960 | CoCrFeNiV Spherical High-entropy Alloy Powder | |
| SP-2087 | Nb-1Zr Alloy Spherical Powder | SP-1877 | Ta-Nb-V-Ti HEA Spherical Powder | |
| SP-2079 | NiAlMo HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1876 | Ta-Nb-Zr-Ti HEA Spherical Powder | |
| SP-2078 | AlCrFeNiCu HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1875 | W-Mo-Ta-Nb-Zr HEA Spherical Powder | |
| SP-2077 | FeCoCrNiMox HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1874 | W-Mo-Ta-Nb HEA Spherical Powder | |
| SP-2076 | (CoCrNi)82Al9Ti9 HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1866 | Mechanical Composite NiCrAlMo Powder | |
| SP-2075 | FeCoCrNiAlx HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1865 | Mechanical Composite NiCrAlCo-Y2O3 Powder | |
| SP-2054 | AlCoCrFeMo HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1864 | AlCoFeNi2.1 HEA Spherical Powder | |
| SP-2040 | Al0.1CoCrFeNiCu0.5 HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1863 | FeCuNiTiAl HEA Spherical Powder | |
| SP-2039 | Al0.3CoCrFeNiMn HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1862 | CoCrNiAlTi HEA Spherical Powder | |
| SP-2038 | Al0.5Cr0.9FeNi2.5V0.2 HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1861 | FeCuAlCrNi HEA Spherical Powder | |
| SP-2037 | Al15Cu28.3Fe28.3Mn28.3 HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1860 | AlCoCrFeNi2.1 HEA Spherical Powder | |
| SP-2036 | AlCoFeCr HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1859 | NiFeCrAlY HEA Spherical Alloy Powder for Thermal Spraying | |
| SP-2035 | (Ni3.5Co3Cr1.5)90Al5Ti5 HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1858 | FeMnCoCrC HEA Spherical Powder | |
| SP-2034 | Ni3.5Co3Cr1.5 HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1857 | NiCrFe10MoWSi HEA Spherical Powder | |
| SP-2033 | NiCrAlTi HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1856 | Ni10Cr6WFe9Ti HEA Spherical Powder | |
| SP-2032 | Fe38Ni32Co10Cr10Al5Ti5 HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1855 | CoCrNiAlTi HEA Spherical Powder | |
| SP-2031 | Fe20Cr20Ni50V4Al2Nb4 HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1854 | NiCoFeCrAlW HEA Spherical Powder | |
| SP-2030 | FeMnAlCrTi HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1853 | NiCrAlMoNbSi HEA Spherical Powder | |
| SP-2029 | FeMnNiCrAl0.5 HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1852 | CoCrNi HEA Spherical Powder | |
| SP-2028 | FeMnNiCr HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1851 | NiMoAl HEA Spherical Powder | |
| SP-2027 | FeCoNiCuAlGa HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1850 | NiCrAl HEA Spherical Powder | |
| SP-2026 | FeCoNiCu HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1848 | NiCrAlY HEA Spherical Powder | |
| SP-2025 | FeCoNiCuAl HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1846 | CoCr(Ni)W HEA Spherical Powder | |
| SP-2024 | FeCoNiAlTi HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1845 | NiCoCrAlY HEA Spherical Powder for Thermal Spraying | |
| SP-2023 | (FeCoNi)86Al7Ti7 HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1844 | CoNiCrAlY HEA Spherical Powder for Thermal Spraying | |
| SP-2022 | Fe45Mn28Co12Cr15 HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1490 | Fe-Co-Ni-Cr-Mo HEA Spherical Powder | |
| SP-2021 | FeCoCrNiCu HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1489 | Fe50Mn30Co10Cr10 Refractory HEA Spherical Powder | |
| SP-2020 | FeCoNi HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1488 | Cu11.85Al3.2Mn0.1Ti Refractory HEA Spherical Powder | |
| SP-2019 | AlCoCrFeNiCu HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1487 | AlCoCr2FeMo0.5Ni Refractory HEA Spherical Powder | |
| SP-2018 | FeCrAl HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1486 | Al32.72Fe9.05Si7.24Mn Refractory HEA Spherical Powder | |
| SP-2017 | FeCoCrNiAl-YHf HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1484 | Fe-Co-Ni-Cr-Mn Refractory HEA Spherical Powder | |
| SP-2016 | FeCrCu Spherical Powder | High-entropy Alloy (HEA) Powder | SP-1483 | Fe-Co-Ni-Cr-Al HEA Spherical Powder | |
| SP-2015 | FeCrNi Spherical Powder | High-entropy Alloy (HEA) Powder | SP-1448 | Cr-Mn-Fe-Co-Ni Refractory HEA Spherical Powder | |
| SP-2014 | (CoCrNi)94Al3Ti3 HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1447 | Cr-Fe-Co-Ni Refractory HEA Spherical Powder | |
| SP-2013 | FeCoNiAlCuTi HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1253 | CoCrMoW Spherical Powder | Cobalt Based Alloys | |
| SP-2012 | FeAlCoCrNiTi HEA Spherical Powder | SP-1252 | CoCrMo Spherical Powder | Cobalt Based Alloys | |
| SP-2011 | Co35Cr35Fe20Al5Ni5 HEA Spherical Powder |
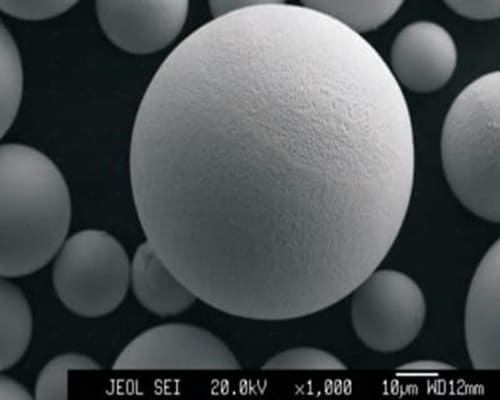
High-Entropy Alloy Powder Morphology
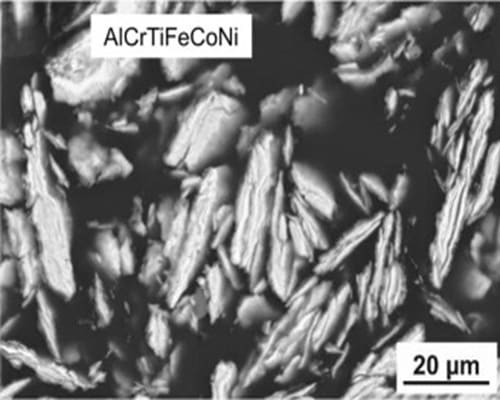
AlCrTiFeCoNi HEA Powder
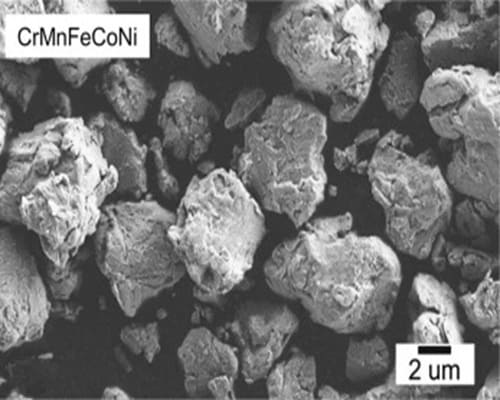
Flaky MorphologyCrMnFeCoNi HEA Powder
Irregular MorphologyWMoTaNbV HEA
Spherical Powder SEMFeCoNiCrTi HEA
Spherical Powder SEM
Top Methods for Producing Spherical Powders
| Production Method | Advantages | Disadvantages | Applications |
| Water Atomization (WA) | – Low cost, suitable for large-scale production – Applicable to various metals and alloys | – Lower sphericity – Powder surface prone to oxidation | Stainless steel, iron-based alloys, etc. |
| Gas Atomization (GA) | – High sphericity and good flowability – Suitable for various metals and high-melting-point materials | – High equipment costs and energy consumption – Use of inert gases increases production costs | Aerospace, medical fields (e.g., titanium alloys, nickel-based superalloys) |
| Plasma Rotating Electrode Process (PREP) | – High powder purity and excellent sphericity – Suitable for reactive metals and alloys (e.g., titanium, zirconium) | – Low production efficiency, suitable for small-scale production – Complex equipment and high costs | High-purity metal powders (e.g., titanium alloys, zirconium alloys) |
| Radio Frequency Plasma Spheroidization | – High sphericity and smooth surface – Suitable for various materials (metals, ceramics, composites) | – Complex equipment and high costs – High energy consumption | High-purity metal powders, ceramic powders (e.g., tungsten, molybdenum, alumina) |
High-Entropy Alloy Spherical Powder Features
- Low oxygen
- High sphericity (≥98%)
- Smooth surface
- No satellite spheres
- Uniform particle size distribution
- Excellent flow properties
- High bulk density and tap density
High-Entropy Alloy Spherical Powder Applicable Process
- Laser/electron beam additive manufacturing (SLM/EBM)
- Injection molding (MIM)
- Hot isostatic pressing (HIP)
- Powder metallurgy (PM)
- Spraying (SP) and other processes
High-Entropy Alloy Powder Applications
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): Used in selective laser melting (SLM), electron beam melting (EBM), or laser cladding to produce complex and high-performance components.
- Powder Metallurgy: Manufacturing bulk HEA materials via hot isostatic pressing (HIP), sintering, or pressing.
- Thermal Spraying and Surface Coating: Used as wear-resistant, corrosion-resistant, or high-temperature coatings through spraying or high-velocity oxy-fuel (HVOF) spraying.
- Aerospace: Manufacturing lightweight, high-strength structure parts, high-temperature components, or oxidation-resistant elements.
- Energy: Producing components for nuclear reactors, high-temperature fuel cell electrodes, or gas turbine parts.
- Extreme Environment: Used to produce functional components for deep-sea, high-temperature, high-pressure, or high-radiation environments.
High-Entropy Alloy Powder Packaging
The High-entropy Alloy Powder products are carefully placed in wooden cases or cartons, with additional support from soft materials, to prevent shifting during transportation. This packaging method guarantees the integrity of the products throughout the delivery process.

Download
Get A Quote
We will check and get back to you in 24 hours.
Other Powder Products
Heeger Metal offers a comprehensive range of metal powder products, including spherical powders, and nano powders. Our high-quality metal powders are ideal for applications in 3D printing, powder metallurgy, electronics, and advanced manufacturing. These powders provide excellent consistency, flowability, and particle size distribution, ensuring superior performance in various industrial processes. Whether you need custom metal powders or standard alloy powders, our products meet the highest quality standards for precision and reliability.